2. Elliptical core fiber#
Elliptical core fibers use an asymmetric core to break the degeneracy between the two linear polarizations of the fundamental mode, via “form birefringence”. Let’s show this. First we’ll design such a fiber.
One of the interesting things about this example is that the accuracy of the computed birefringence in the fundamental mode seems particularly sensitive to the rate at which mesh elements are allowed to change in size; you can test this effect by changing the meshing parameters Waveguide.mesh_dist_power and/or Waveguide.mesh_dist_scale.
First, we’ll construct the elliptical core fiber. Parameters are loosely based off of FiberLabs ZEF-2.2×5.5/125-N. Since polarization is important, we’ll ultimately use the vectorial solver, and need to generate an order 1 mesh.
from wavesolve import waveguide
## params
ncore = 1.512
nclad = 1.474
acore = 5.5/2 # core semimajor axis
bcore = 2.2/2 # core semiminor axis
rclad = 12. # outer boundary radius
core_res = 64 # resolution for core boundary
clad_res = 32 # resolution for outer boundary
## make the fiber
core = waveguide.Ellipse(ncore,"core")
core.make_points(acore,bcore,core_res)
clad = waveguide.Circle(nclad,"cladding")
clad.make_points(rclad,clad_res)
ellipfiber = waveguide.Waveguide([clad,core])
# make order 1 mesh
mesh = ellipfiber.make_mesh(order=1)
# only plot mesh lines
ellipfiber.plot_mesh(mesh,plot_points=False)
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
Now, we’ll solve for the modes.
from wavesolve.FEsolver import count_modes,plot_vector_field,solve_waveguide_vec,get_eff_index
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt, numpy as np
wl = 1.55 # wavelength
IOR_dict = ellipfiber.assign_IOR()
ws,vs = solve_waveguide_vec(mesh,wl,IOR_dict,Nmax=4)
ne = get_eff_index(wl,ws) # convert all eigenvals into effective indices
# plotting
fig,axs = plt.subplots(2,2,sharex=True,sharey=True,figsize=(8,8))
for i,ax in enumerate(axs.flatten()):
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.set_title(r"$n_{\rm eff}=$"+str(round(np.real(ne[i]),5)))
plot_vector_field(mesh,vs[i],show_mesh=False,ax=ax,bounds=(-5,5,-5,5))
ellipfiber.plot_boundaries(ax) # show the core-cladding boundary
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0)
plt.show()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
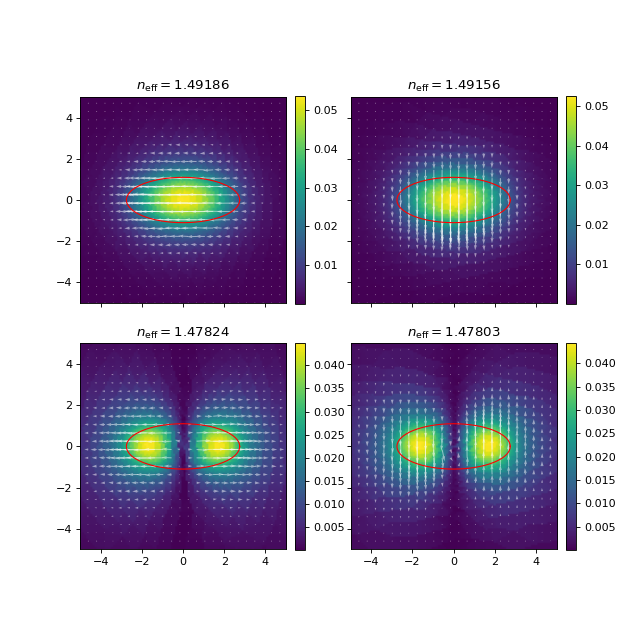
This fiber supports four guided modes, but the latter two might be lossy since they extend further into the cladding. The birefringence is around \(3\times 10^{-4}\), which seems reasonable (I could not find a spec on the manufacturer’s site except for a comment that typical birefringence for these types of fibers is above \(10^{-4}\)).